Latest

Climate pledges could shrink global cropland
The tradeoff raises concerns about food security, particularly for the Global South.
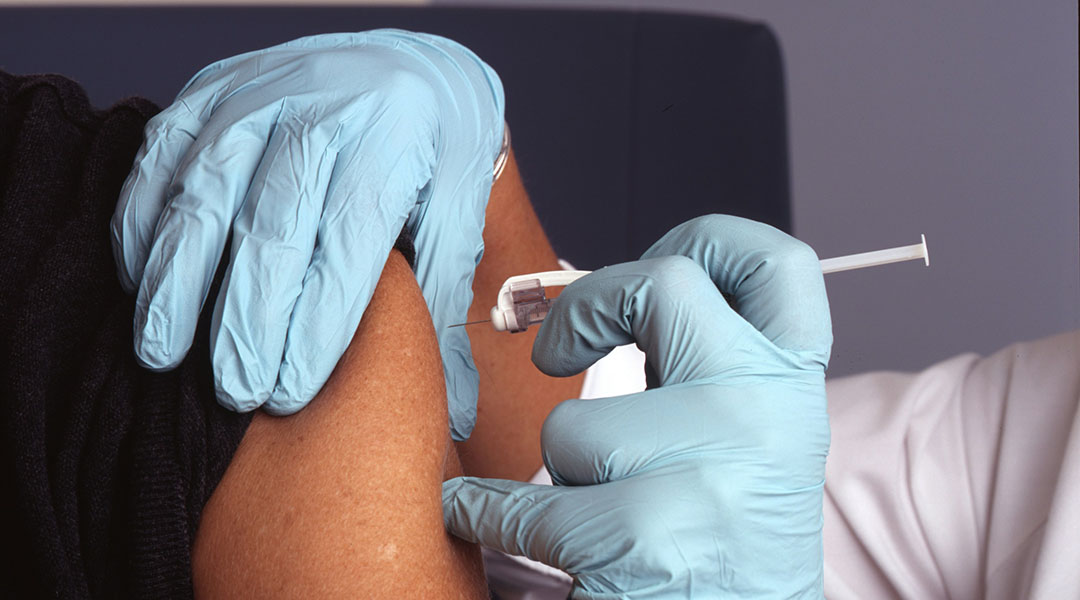
Two-in-one nanomedicine delivers antiviral treatment and immediate vaccine-like protection
The quasi-vaccine could help healthcare workers weather a virus outbreak in the future.
Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.

Self-interacting inflaton particles may reshape our picture of the early universe
Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.
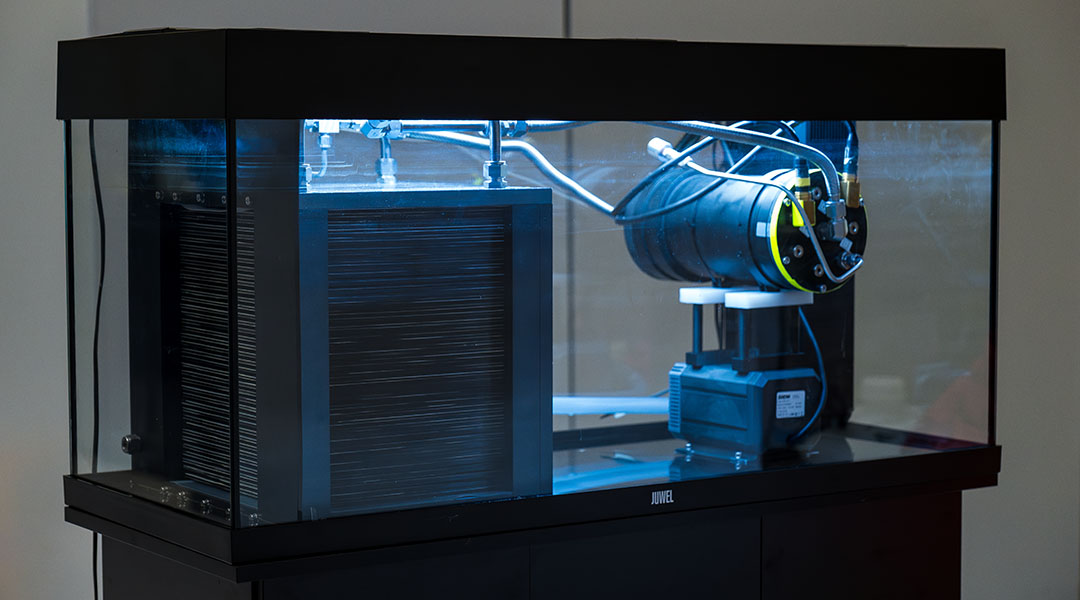

New fuel cell is equipped with gills for autonomous underwater vehicles
A fish-inspired fuel cell concept could provide a cost-effective alternative to batteries in underwater vehicles.

Climate pledges could shrink global cropland
The tradeoff raises concerns about food security, particularly for the Global South.

Two-in-one nanomedicine delivers antiviral treatment and immediate vaccine-like protection
The quasi-vaccine could help healthcare workers weather a virus outbreak in the future.
ASN Weekly
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.
Ultra-dense electron beams set the stage for breakthroughs in physics and technology
SLAC scientists created ultra-dense electron beams with five times the peak current, using infrared lasers to unlock new frontiers in physics and materials research.

Solar panels made of lunar dust could power a future Moon base
Making solar panels on the Moon could be the solution to reliably providing energy to lunar settlements.

Sustainable building material extracted from seawater
A sand-like material can be extracted from seawater by adding carbon dioxide, potentially making the building industry more sustainable.
World’s smallest pacemaker dissolves once it’s no longer needed
Smaller than a grain of rice, the pacemaker is designed with temporary interventions in mind.

New machine learning tool could transform how we study neutron star mergers
A new machine learning algorithm that can rapidly pinpoint the location of a neutron star merger using gravitational wave signals alone.

Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.

Self-interacting inflaton particles may reshape our picture of the early universe
Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.

New fuel cell is equipped with gills for autonomous underwater vehicles
A fish-inspired fuel cell concept could provide a cost-effective alternative to batteries in underwater vehicles.

Ultra-dense electron beams set the stage for breakthroughs in physics and technology
SLAC scientists created ultra-dense electron beams with five times the peak current, using infrared lasers to unlock new frontiers in physics and materials research.

Claudia Loebel, understanding cell memory could lead to patient-specific treatments
Recreating the material that surrounds cells, Loebel aims to better understand cell memory and its role in disease development.

Haruka Sasaki, uncovering the link between melatonin and asthma
Haruka Sasaki is researching how melatonin impacts asthma to create new treatments for life-threatening nocturnal attacks.

Riccardo Bassoli: How quantum computing will redefine wireless communication
Future 6G wireless networks will rely on quantum computers, but developing the technology and making it sustainable is complex.

Rose Marks, a botanist studying resurrection plants
Rose Marks uses her climbing skills in remote regions of South Africa to study how water-deprived plants might help develop drought-tolerant crops.

Claudia Loebel, understanding cell memory could lead to patient-specific treatments
Recreating the material that surrounds cells, Loebel aims to better understand cell memory and its role in disease development.

Haruka Sasaki, uncovering the link between melatonin and asthma
Haruka Sasaki is researching how melatonin impacts asthma to create new treatments for life-threatening nocturnal attacks.

Two-in-one nanomedicine delivers antiviral treatment and immediate vaccine-like protection
The quasi-vaccine could help healthcare workers weather a virus outbreak in the future.

World’s smallest pacemaker dissolves once it’s no longer needed
Smaller than a grain of rice, the pacemaker is designed with temporary interventions in mind.

Scientists discover a new class of antibiotics
A bacterium found in a backyard could offer new hope in the fight against antibiotic resistance.
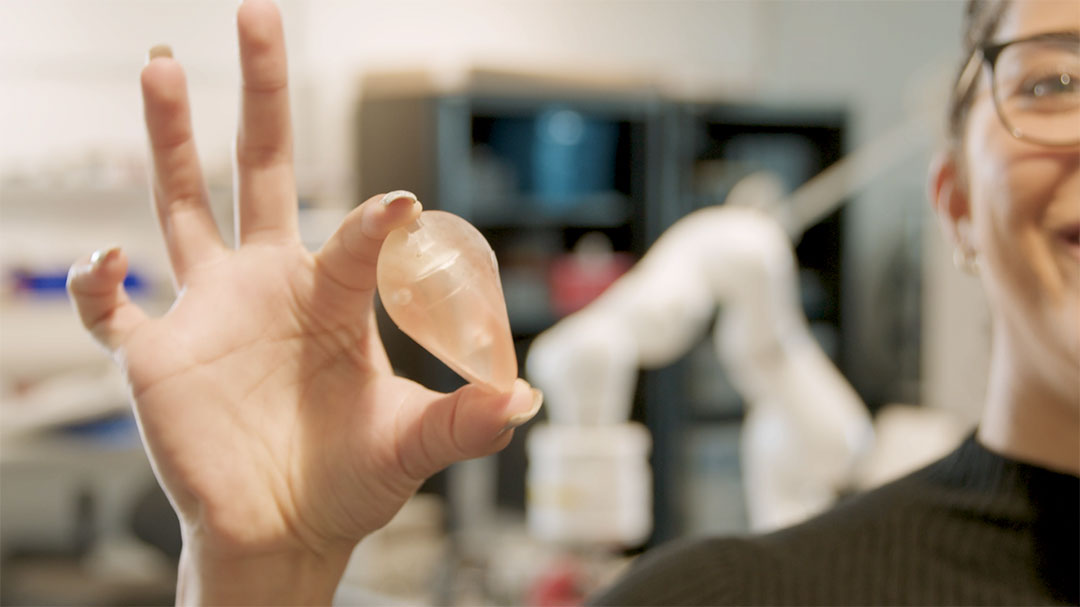
Tiny robots take 3D scans from inside the gut to diagnose cancer
A robot with a unique shape could make it possible to perform ultrasound scans deep within the gut, helping doctors diagnose colorectal cancer.

Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.

New fuel cell is equipped with gills for autonomous underwater vehicles
A fish-inspired fuel cell concept could provide a cost-effective alternative to batteries in underwater vehicles.

Solar panels made of lunar dust could power a future Moon base
Making solar panels on the Moon could be the solution to reliably providing energy to lunar settlements.

New machine learning tool could transform how we study neutron star mergers
A new machine learning algorithm that can rapidly pinpoint the location of a neutron star merger using gravitational wave signals alone.

Climate pledges could shrink global cropland
The tradeoff raises concerns about food security, particularly for the Global South.

Sustainable building material extracted from seawater
A sand-like material can be extracted from seawater by adding carbon dioxide, potentially making the building industry more sustainable.
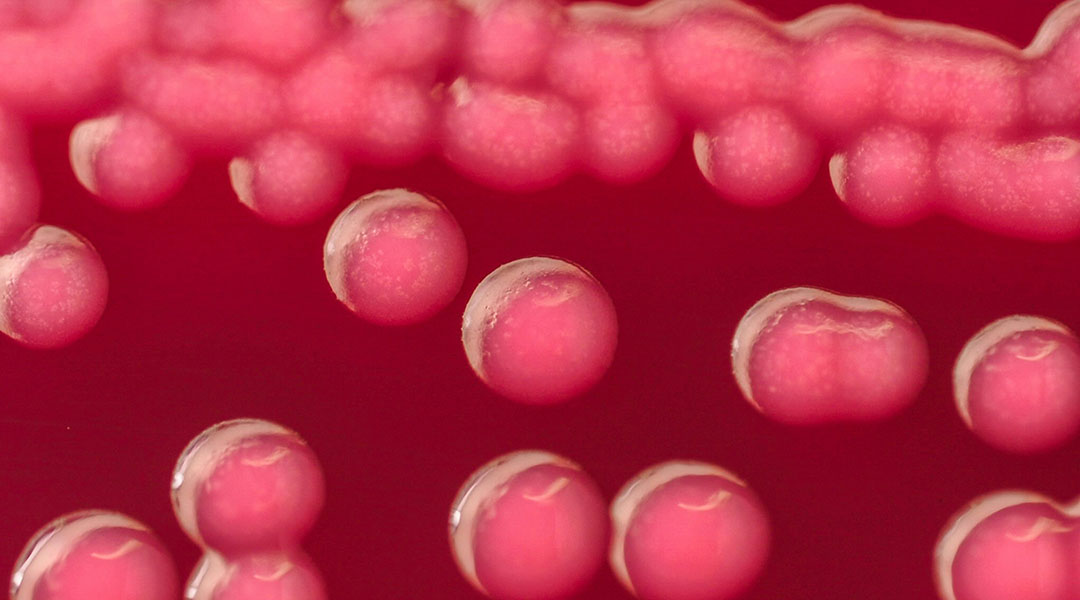
Common bacteria could be used to produce biodegradable bioplastics
Engineered Escherichia coli bacteria could be used to make sustainable biobased plastics.

Microplastics could be hotspots for antimicrobial resistance
Microplastics facilitate a “super slime” that is resistant to antibiotics, sparking concern about antibiotic resistance in heavily polluted areas.

Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.

Self-interacting inflaton particles may reshape our picture of the early universe
Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.

Ultra-dense electron beams set the stage for breakthroughs in physics and technology
SLAC scientists created ultra-dense electron beams with five times the peak current, using infrared lasers to unlock new frontiers in physics and materials research.

Solar panels made of lunar dust could power a future Moon base
Making solar panels on the Moon could be the solution to reliably providing energy to lunar settlements.





